Benefits of Temperature Cycle Testing for Product Reliability
In today’s competitive market product reliability is paramount for maintaining a strong brand reputation. Temperature Cycle Testing is a key method to ensure durability, simulating extreme temperature conditions to identify potential weaknesses before products reach consumers.
By understanding and implementing this testing, manufacturers can enhance product reliability, avoid costly recalls, and stay ahead in the market. Let’s explore how temperature cycle testing can elevate product performance and safeguard brand trust.
Importance of Product Reliability in Today’s Market
Product reliability is essential in today’s market because it directly influences a brand’s reputation, customer retention, and long-term success. As consumers have access to more information, their expectations for performance, durability, and consistency have risen significantly.
A product failure can lead to negative reviews, social media backlash, and a loss of customer trust—an issue that’s difficult to recover from in a highly competitive marketplace.
When brands focus on delivering reliable products, they foster trust and loyalty, which not only encourages repeat business but also drives positive word-of-mouth, which is invaluable for growth. A dependable product also reduces the likelihood of costly issues like returns, warranty claims, and customer service complaints, ensuring the brand can allocate resources more efficiently.
Ultimately, the emphasis on product reliability is an investment in a brand’s long-term stability, as it maintains consumer confidence and helps mitigate risks associated with poor product performance.
What is Temperature Cycle Testing and How Does it Work?
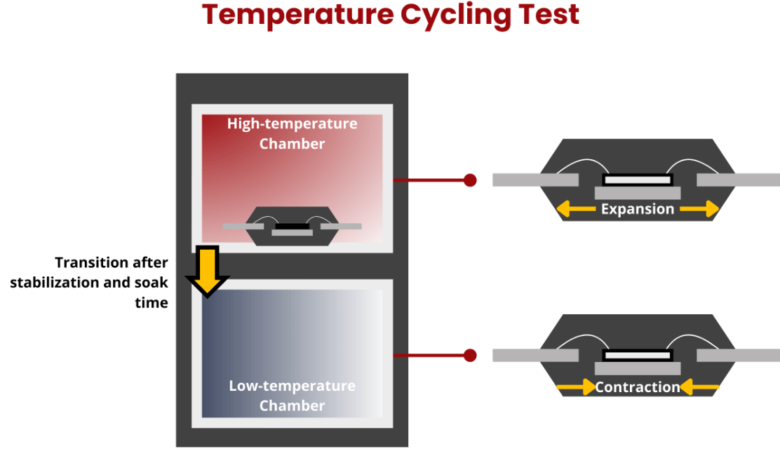
Temperature cycle testing is an important evaluation process to determine how well a product can withstand extreme temperature variations. It simulates the environmental conditions a product might experience in real-world scenarios, ranging from intense heat to cold, ensuring that the product remains functional and reliable under diverse conditions.
How Temperature Cycle Testing Works
- Product Placement: The item is positioned in a specialized chamber that can rapidly alter its internal temperature. This feature enables the chamber to swiftly transition between high and low temperatures, simulating the extreme environments that the product may encounter.
- Temperature Cycles: The product undergoes repeated cycles of heating and cooling. These temperature changes vary in intensity and duration based on the specific needs and expected operating conditions of the product. For example, the product might go through multiple cycles of high heat followed by cold, simulating exposure to fluctuating outdoor conditions.
- Performance Monitoring: During the test, engineers closely monitor various performance metrics, such as material integrity, functionality, and potential deformation or failure. Sensors may track things like expansion, contraction, and any mechanical or electronic malfunctions that could occur due to temperature changes.
- Detection of Weaknesses: The goal is to identify signs of stress, cracks, or failure that may develop during these cycles. These insights help manufacturers pinpoint weaknesses in the product’s design, materials, or components that could compromise its performance in real-world applications.
Importance of Temperature Cycle Testing
This testing method is crucial for manufacturers looking to improve the durability and reliability of their products under varying environmental conditions. By identifying potential failure points early in the design process, temperature cycle testing helps ensure that products can withstand harsh conditions over the long term, enhancing their longevity and overall performance.
Read also: Apple Intelligence: Your Personalized Tech Assistant
Benefits of Temperature Cycle Testing for Product Reliability
Temperature cycle testing plays an important role in ensuring product reliability by subjecting products to extreme temperature fluctuations. This process helps manufacturers gain valuable insights into how materials and components perform under stress, ultimately enhancing product design, durability, and market competitiveness.
1. Identifies Weaknesses in Product Design
One of the key benefits of temperature cycle testing is its ability to reveal hidden weaknesses in product design. By exposing products to rapid temperature shifts, engineers can identify critical flaws, such as material expansions, contractions, or brittle components that might fail under real-world conditions. This early detection allows for necessary design modifications before mass production, reducing the risk of failures in the field and enhancing the overall product quality.
2. Predicts Potential Failures in the Field
Temperature cycle testing is also instrumental in predicting how products will perform over time in real-world environments. By simulating the environmental conditions that a product will experience, manufacturers can identify vulnerabilities like cracks or weak joints that might not be apparent during standard production. This proactive approach ensures that products are designed to withstand the stresses they encounter, ultimately preventing costly recalls and warranty claims.
3. Ensures Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is critical for market success, particularly in sectors where safety and performance are paramount. Temperature cycle testing helps manufacturers validate that their products meet these strict criteria. By ensuring that products adhere to safety and reliability standards, businesses not only avoid potential legal issues but also build customer trust. Knowing that a product has passed rigorous testing increases consumer confidence in its performance.
4. Saves Time and Money in the Long Run
While temperature cycle testing involves an initial investment, it saves time and money. Early detection of design flaws allows manufacturers to address issues during the development phase, which is far less costly than dealing with product recalls or repairs after launch. Additionally, products that endure extensive temperature cycling tend to last longer, reducing the need for replacements and increasing customer satisfaction. The time saved from early flaw detection also accelerates time-to-market, giving businesses a competitive edge.
Temperature cycle testing is an invaluable tool for manufacturers aiming to improve product reliability, ensure compliance with industry standards, and enhance customer satisfaction. By investing in this testing, businesses can prevent costly failures, reduce warranty claims, and foster long-term trust.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Temperature Cycle Testing
Temperature cycle testing has proven essential across various industries for improving product reliability and durability. Here are a few real-life examples:
- Smartphone Industry: A leading smartphone manufacturer used temperature cycle testing to assess battery performance under extreme temperature fluctuations. The testing revealed weaknesses in battery longevity and charging efficiency, leading to design changes that improved battery life and reduced overheating. This proactive testing enhanced device reliability, customer trust, and reduced warranty claims.
- Aerospace Industry: An aerospace manufacturer used temperature cycle testing to simulate the extreme conditions of high-altitude flight on critical components like engine parts and control surfaces. The testing identified potential failures, allowing the company to refine designs and choose better materials, ensuring safer and more reliable aircraft.
- Automotive Industry: A car manufacturer tested the performance of electronic control units (ECUs) in their vehicles under extreme temperatures. This testing highlighted failure points, leading to design improvements that enhanced ECU durability and overall vehicle performance. The result was a more reliable vehicle, boosting customer satisfaction and brand trust.
These examples demonstrate the value of temperature cycle testing in enhancing product durability, safety, and performance. By identifying weaknesses early, companies can improve their products, reduce risks of recalls or warranty claims, and strengthen their brand reputation.
Tips for Conducting Effective Temperature Cycle Testing
Temperature cycle testing is essential for ensuring product durability and reliability. To maximize its effectiveness, follow these key steps:
- Define Clear Objectives: Set specific performance parameters to focus the testing on relevant aspects like battery life or material durability.
- Select the Right Test Chamber: Choose a chamber that replicates real-world temperature conditions, ensuring accurate and consistent testing.
- Monitor and Document: Track changes in physical properties and document signs of wear or failure during temperature fluctuations.
- Run Multiple Cycles: Conduct several cycles to simulate long-term stress and gain more reliable insights into the product’s durability.
- Analyze Data Thoroughly: Look for patterns that may reveal potential design flaws or weaknesses in product performance.
- Involve Cross-Functional Teams: Collaborate with design, engineering, and quality control teams to gain diverse perspectives on the results.
By following these steps, manufacturers can identify weaknesses early, improve product quality, and reduce the risk of failures, ultimately leading to more reliable products.